Uterine fibroids are noncancerous growths in the uterus muscle tissue, affecting 70-80% of women. While most don't show symptoms, larger fibroids may impact fertility. Fertility specialists can assess and recommend treatment, but small fibroids may not require intervention, with a generally positive prognosis.
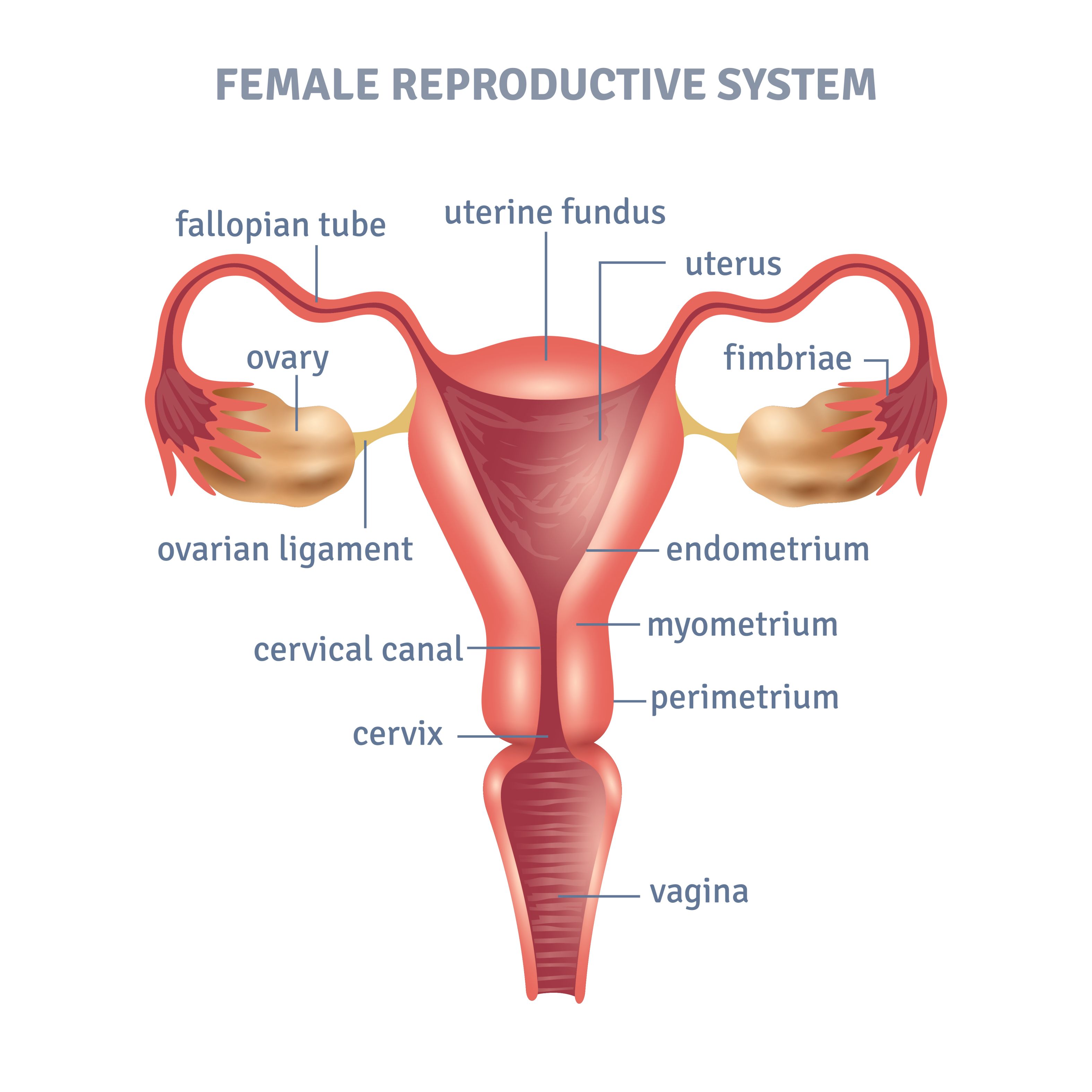
Uterine fibroids are benign smooth muscle tumors affecting about 20% of women of reproductive age. Also known as leiomyomas or myomas, they do not pose an elevated risk of uterine cancer, and the chances of fibroids developing into cancer are extremely low. Fibroids are a common type of tumor in the reproductive tract and are often discovered during routine pelvic exams. Many women with fibroids experience little to no symptoms, but some may have heavy periods, pelvic pain, or bleeding between periods.
The exact cause of fibroids is unknown, but several factors may contribute:
Many women with fibroids don't experience symptoms, but common ones include:
Routine pelvic exams can detect irregularities in the uterus shape. Tests include ultrasound scans, lab tests, and imaging tests like MRI, Hysterosonography, Hysterosalpingography, or Hysteroscopy if ultrasound results are inconclusive.
The approach to treatment varies, with options such as watchful waiting, medications (GnRH agonists, progestin-releasing IUD, contraceptives, NSAIDs), and surgery (hysterectomy or myomectomy). The choice depends on the size, symptoms, and individual circumstances.
Fibroids can impact fertility by altering the cervix shape, hindering sperm entry, changing the uterus shape, blocking fallopian tubes, affecting the uterine cavity lining, and decreasing blood flow. However, not all fibroids lead to infertility.
Uterine fibroids are common benign tumors in women of reproductive age. Many women may have them without symptoms, while in some cases, fibroids can affect fertility and hinder pregnancies. Early detection and appropriate management can help address any concerns related to uterine fibroids.